What is an IPBX?
The IPBX is an advanced business communications management solution that combines voice and data within an integrated IP network. In practical terms, the IPBX replaces traditional telephone systems by using IP technologies to route calls and manage internal and external communications.
The role of VoIP
At the heart of the IPBX lies VoIP, or Voice over IP, a technology that enables voice to be transmitted as data over the Internet.
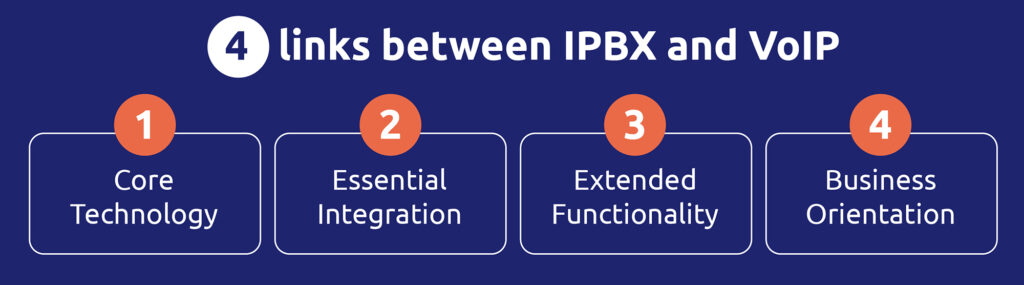
The link between IPBX and VoIP is essential and can be understood in 4 simple ways:
- Core technology: VoIP is the technology that enables voice to be transmitted over IP networks, such as the Internet. The IPBX uses this technology to route telephone calls, which means that VoIP is how the IPBX carries out voice communications over the network.
- Essential integration: VoIP can be seen as the centerpiece of the IPBX. While VoIP focuses on voice transmission over the Internet, the IPBX represents a complete communications management system that leverages VoIP for its calls.
- Extended functionality: VoIP is limited to voice transmission, while the IPBX offers a wide range of call management features, such as call waiting, call transfer, conference calling, voicemail, and more. All are possible by VoIP technology.
- Business orientation: VoIP can be used by both private individuals and businesses for calls via the Internet. The IPBX, on the other hand, is specifically designed to meet the business needs of enterprises by providing a complete, professional communications solution, leveraging VoIP technology for its communications.
In a nutshell, VoIP is the technology that enables voice transmission over the Internet, and the IPBX is a system that exploits this technology to provide advanced communication services specifically designed for businesses.
The PABX: Foundation and transition to the IPBX
To understand the importance of the IPBX, it’s essential to start by talking about the PABX. The PABX, or Private Automatic Branch Exchange, is a private telephone system used within companies to manage internal and external telephone communications.
The IPBX represents a natural evolution from the PABX, resulting from the need for a modern, adaptable communications infrastructure. Whereas the traditional PBX relies on conventional telephone lines, the IPBX takes full advantage of the benefits of IP networks. This transition marks a significant evolution towards more efficient business communications, meeting the dynamic needs of today’s enterprises.
How an IPBX works
To fully understand how the IPBX works, let’s first look at how it fits into the heart of the company’s internal network.
Internal network connection
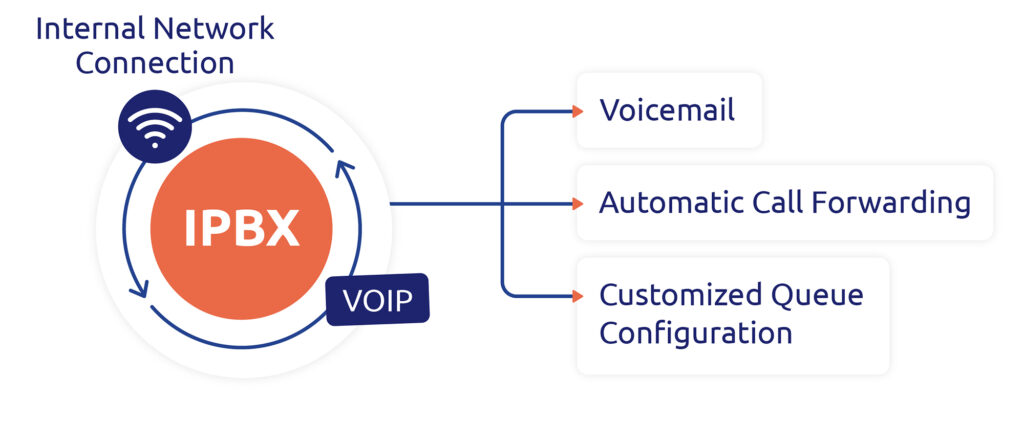
The IPBX integrates with the company’s internal network to orchestrate centralized communications management. This internal connection is the foundation of its operation, enabling optimal call distribution within the organization.
VoIP integration
At the heart of the system, the IPBX draws its efficiency from integrating VoIP (Voice over IP). This innovative technology transforms voice into digital data and transmits it via the IP network. This approach optimizes bandwidth use, guaranteeing good sound quality and unlocking advanced features.
Centralized management
The IPBX, by leveraging the connection to the internal network and the power of VoIP, offers powerful centralized communications management. This centralization enables the implementation of advanced features such as voicemail, automatic call forwarding, and the customized queue configuration. This unified approach contributes to a seamless user experience and increased flexibility in enterprise communications management.
Trunk SIP: Optimizing communications
Trunk SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) is the external link, connecting the IPBX to the public telephone network or other communications systems. Trunk SIP enables flexible connectivity, facilitating the two-way exchange of calls.
Its use offers a cost-effective, scalable solution, enabling companies to optimize communications while maintaining a flexible, adaptable architecture.
IPBX benefits
Reduce telephony costs
The IPBX significantly reduces telephony costs by optimizing existing IP networks. Free internal calls and reduced rates for external calls enable companies to significantly reduce their telephone bills, freeing up financial resources for other strategic investments.
Integrating VoIP with CRM
Tight integration of VoIP with customer relationship management (CRM) systems offers a competitive advantage. This collaboration gives customer service teams instant access to customer data during calls, facilitating a faster, more personalized response, thus boosting customer satisfaction and loyalty.
CTI (Computer Telephony Integration)
CTI represents a significant IPBX advantage, seamlessly integrating IT and telephone systems. This convergence facilitates advanced functionalities, such as automatic ticket creation on incoming calls, improving operational efficiency and reinforcing the integrity of customer data.
Potential disadvantages of IPBX
Dependence on Network Infrastructures
The IPBX can introduce a critical dependency on network infrastructures. Any malfunction or interruption in Internet connectivity can compromise communications. Robust planning and redundancy mechanisms are therefore essential to mitigate these risks.
VoIP security issues
VoIP IPBX can be vulnerable to security threats such as Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks or call interception. Implementing robust security protocols and regular updates is crucial to mitigating these risks.
Complexity of Technical Management
Advanced IPBX management may require specific technical skills. Configuration, maintenance, and troubleshooting often require specialized expertise, which can increase labor costs and necessitate investment in staff training.
The differences between IPBX and PABX
The PABX operates by routing telephone calls within the company and providing features such as voicemail, call forwarding, call waiting, and the ability to dial internal numbers without using the public telephone network.
The PABX is designed to improve communications efficiency by enabling users to share several telephone lines while retaining advanced call management features.
Although the PABX is still in use, it is gradually being replaced by more modern technologies such as the IPBX (Internet Protocol-based Private Branch Exchange), which exploits IP networks for more flexible, cost-effective communications.
Architecture and Infrastructure
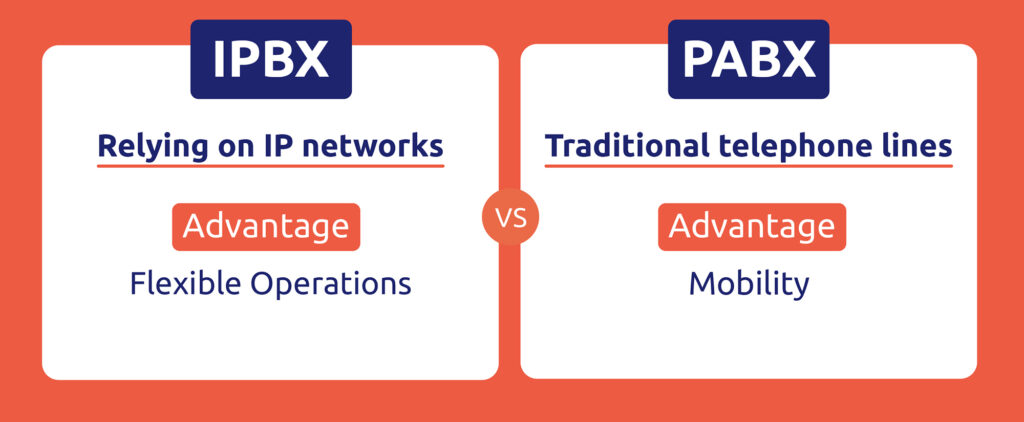
The first major distinction between IPBX (IP-based Private Branch Exchange) and PABX (Private Automatic Branch Exchange) lies in their underlying architecture and infrastructure. The PABX uses conventional telephone lines, while the IPBX exploits IP networks to transmit voice as digital data. This fundamental difference influences not only the quality of communications but also the range of features available.
Flexibility and mobility
A significant difference between IPBX and PABX lies in their flexibility and ability to support mobility. The IPBX, relying on IP networks, enables extensive connectivity, allowing users to access telephone services seamlessly from remote locations. However, mobility is different from IPBX’s strong point, as it requires physical installation.
The PABX dependence on traditional telephone lines also offers limited mobility, which can be a limiting factor for modern businesses focused on flexible operations.
Communications costs
A crucial aspect differentiating IPBX from PABX is the cost of communications. The IPBX generally offers advantageous or even free rates for internal calls, exploiting existing IP networks. PABXs, on the other hand, which rely on traditional telephone lines, often involve higher costs, particularly for external calls. This economic disparity is decisive for companies looking to optimize their telephone costs.
In short, while the PABX has long been the standard for enterprise telephone systems, the IPBX represents a significant evolution, capitalizing on the advantages of IP networks. These key differences in architecture, flexibility, and cost position the IPBX as a modernized solution adapted to the changing needs of today’s businesses.
IPBX or Centrex: which to choose?
Centrex (Central Exchange) is an outsourced business telephony service where the switching infrastructure and telephony features are managed by a service provider. Users connect to the provider’s network to access telephone services, offering an outsourced solution to a company’s communication needs.
Centrex and IPBX are two approaches to enterprise communications management, but they differ mainly in their architecture and location of switching equipment.
Infrastructure flexibility
When choosing between IPBX (Internet Protocol-based Private Branch Exchange) and Centrex, infrastructure flexibility is an essential criterion. With IPBX, the infrastructure can be deployed in-house, giving the company direct control. On the other hand, Centrix outsources the entire infrastructure to the service provider, limiting the company’s direct personalization and control over its telephone services. Mobility is therefore a significant advantage of Centrex.
Functionality Control
One of the major points of difference is the level of control over telephony functionality. IPBXs offer greater flexibility, enabling companies to customize features and make in-house upgrades without constantly relying on the supplier. Conversely, Centrex delegates feature management to the supplier, limiting the company’s ability to make changes quickly and autonomously.
Cost and Financial Flexibility
The choice between IPBX and Centrex also involve financial considerations. IPBXs can incur initial investment costs, especially when deployed in-house, but often offer greater financial flexibility in the long term. Centrex costs are generally based on usage, which can be advantageous for companies with fluctuating communication needs, although this can lead to financial dependence on the supplier.
In conclusion, the choice between IPBX and Centrex depends on the specific needs of each company. The IPBX may be the ideal solution if flexibility and direct control are priorities. On the other hand, if simplicity and outsourced management are preferred, Centrex may offer a practical alternative.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the IPBX is proving to be a major evolution in corporate communications management, offering benefits such as reduced costs and uniform call quality. However, precautions are needed due to dependence on network infrastructures and potential security challenges. Comparison with PABX underlines the need for a transition to modern solutions.
As for the choice between IPBX and Centrex, the flexibility and direct control of the IPBX make it the preferred choice.
Request a personalized demo with Diabolocom today to discover how our solution can transform your communications management, improve operational efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Want to find out more about IPBX?



