What is VoIP?
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) encompasses the transmission of voice and data over IP networks, enabling efficient, cost-effective communications via the Internet or a local private network such as an intranet. Its diverse applications, from videoconferencing to voice messaging, offer businesses powerful tools for remote communication.
VoIP can be used via the wired network (Ethernet, fiber optics or ADSL) or the wireless network: Wi-Fi, 3G, 4G, 5G.
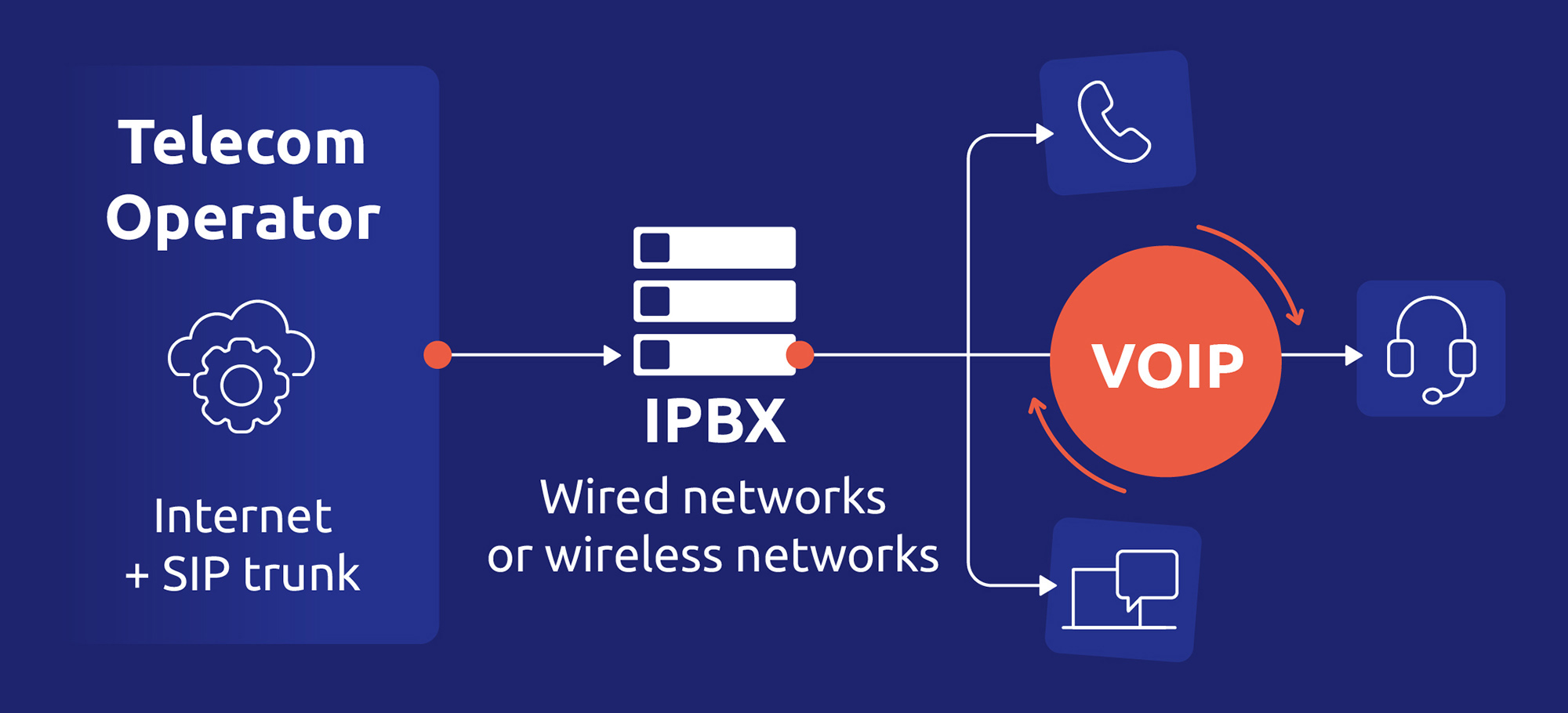
A brief history of VoIP
Its beginnings date back to the first experiments in the 1970s, but it was in the 1990s that VoIP began to gain notoriety. In its early days, it relied mainly on protocols such as H.323, seeing the emergence of SIP (Session Initiation Protocol), which helped standardize and simplify voice communications over the Internet.
VoIP application with Skype and Zoom
VoIP has grown exponentially thanks to iconic platforms such as Skype and Zoom.
Skype, launched in 2003, revolutionized personal communication by offering free voice and video calls over the Internet, eliminating geographical barriers for millions of users worldwide.
Meanwhile, Zoom, which appeared more recently in 2013, has emerged as a critical player in business videoconferencing, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic. These two giants have played a crucial role in the democratization VoIP, demonstrating its simple and robust communications capabilities.

The advantages and limitations of VoIP
VoIP offers many significant advantages that have contributed to its widespread adoption in both professional and personal environments.
Cost reduction is one of the significant advantages, with international calls often less expensive than traditional PSTN telephony solutions.
Flexibility is also an asset, enabling users to communicate via various Internet-connected devices, from computers to smartphones.
VoIP offers advanced features such as voicemail, videoconferencing, and centralized call management, improving the efficiency of business communications.
However, VoIP has its limitations.
Its dependence on a stable Internet connection can lead to audio quality problems when bandwidth is low or irregular. In the event of a power cut or network failure, VoIP can become inoperable, underscoring the need for redundancy and proper planning. Security is also an issue, as voice data transits via the Internet, requiring robust protection measures to prevent potential attacks.
What is ToIP?
Telephony over IP (ToIP) is a significant evolution in telephone communications, where voice is transmitted as digital data over IP (Internet Protocol) networks. Unlike traditional systems, ToIP uses existing IT infrastructures to route calls, messaging, videoconferencing, and data transmission, eliminating the need for dedicated telephone lines. This convergence of voice and data opens up new horizons, enabling seamless integration with other corporate IT applications without needing a PSTN or mobile network.
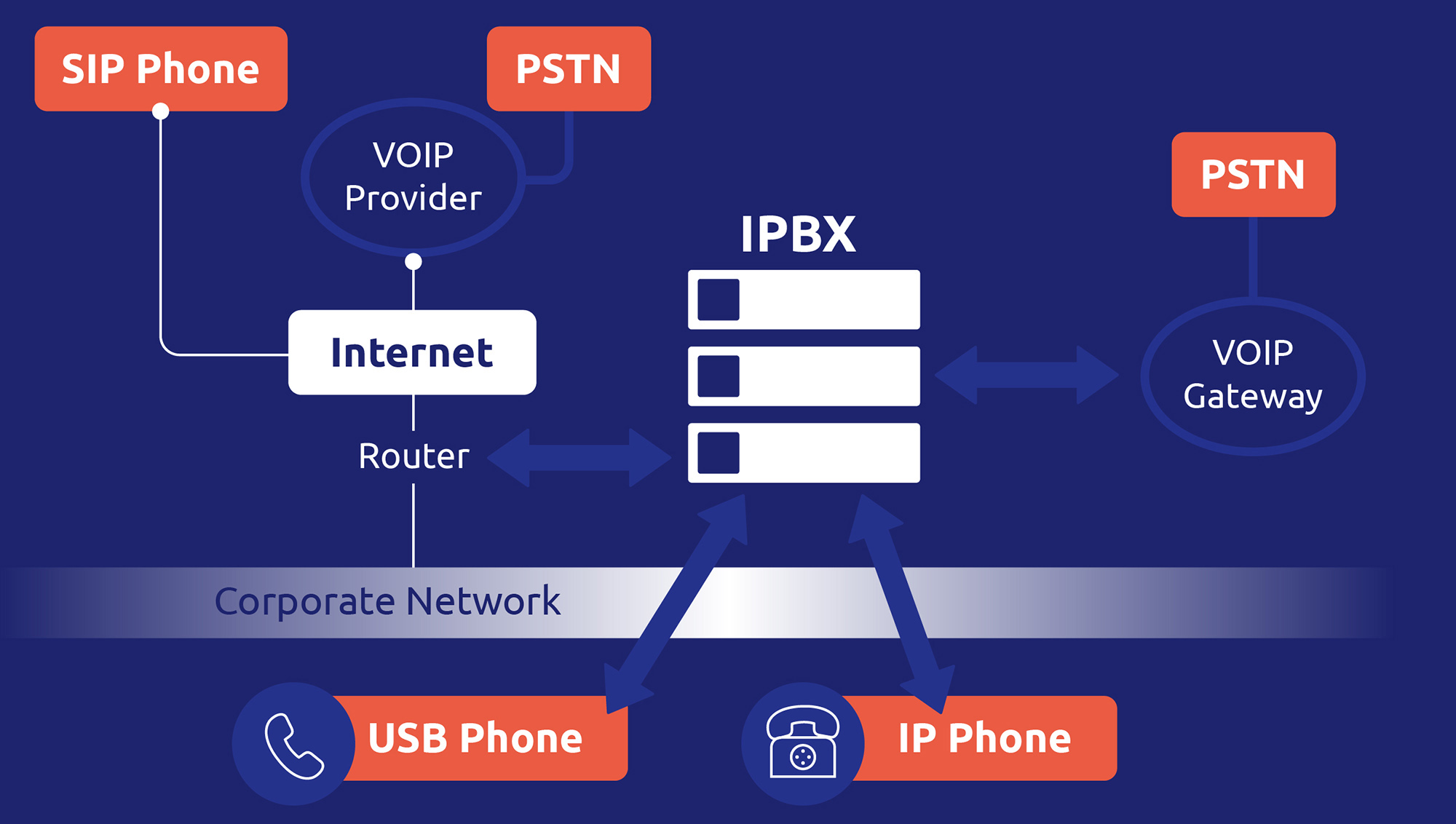
How has ToIP evolved from VoIP?
While VoIP laid the foundations by enabling voice transmission via Internet protocols, ToIP goes further by integrating telephony into the overall IT environment. In other words, where VoIP focuses primarily on voice transmission via the Internet, ToIP embraces a more holistic approach by integrating telephony into a company’s overall IT ecosystem.
ToIP applications in professional environments
ToIP unifies voice communications and data services, utilizing existing network infrastructures and IT applications.This convergence offers closer integration with enterprise management systems. It goes beyond simple voice transmission to provide advanced features such as unified messaging, video conferencing, and seamless communications integration within business processes.
This transition from VoIP to ToIP reflects a more integrated and strategic approach to business communications. It represents a step towards smoother connectivity and improved collaboration within organizations while continuing to capitalize on the fundamental advantages of VoIP.
Specific advantages and limitations of ToIP
ToIP offer a plethora of specific advantages that transcend simple voice transmission capabilities.
Firstly, tight integration with enterprise management systems enables greater automation of processes, improving operational efficiency. Unified messaging simplifies information management, reducing response times and boosting productivity.
ToIP also offers advanced conferencing capabilities, enabling efficient collaboration across geographically distributed teams. However, it is crucial to note that ToIP is generally limited to fixed SIP terminals, such as IP phones or softphones connected to computers. Unlike VoIP, ToIP has restrictions on its use on mobile devices such as smartphones or tablets, both inside and outside the company.
However, a significant drawback of ToIP is that it is limited to fixed SIP terminals, thus restricting the mobility of professionals. The impossibility of using ToIP on smartphones or tablets represents an obstacle, particularly for employees on the move or those not connected to the local network.
The role of a ToIP communication protocol
The operation of a Telephony over IP (ToIP) communication protocol is based on complex processes designed to ensure the efficient transmission of voice data over IP networks.
One of the fundamental protocols used is SIP (Session Initiation Protocol). When a user initiates a call, SIP sets take charge of setting up the session and exchanges information such as IP addresses and codecs for audio compression. Once the session has been established, RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) transport audio data between the parties in real-time, guaranteeing smooth transmission.
The Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) is involved in real-time transport of audio data, ensuring that it is optimally routed between the parties. Quality of service management protocols, such as DiffServ (Differentiated Services).
In short, the operation of a ToIP communication protocol revolves around the initiation of sessions, the negotiation of audio parameters, and the real-time transport of voice data, thus ensuring reliable, high-quality communication within the digital environment.
What’s the difference between VoIP and ToIP?
The distinction between ToIP and VoIP is a fine one. ToIP concerns only the internal network, while VoIP refers to the transmission of IP communication data across different actors such as individuals, companies, and service providers.
Telephony over IP (ToIP) and Voice over IP (VoIP) share the fundamental basis of voice transmission over IP networks but differ in specific technical and practical aspects.
The technical and practical differences between VoIP and ToIP
From a technical point of view, ToIP goes beyond simple voice transmission, integrating telephony into the overall IT ecosystem. It is characterized by closer integration with business management systems, enabling greater automation of processes and smoother collaboration.
In practical terms, VoIP is often used more informally for personal communications, while ToIP is often deployed in business environments where deeper integration with other applications is crucial. ToIP also offers advanced features such as unified messaging, conference calling, and seamless integration with other systems, reinforcing its usefulness in complex business contexts.
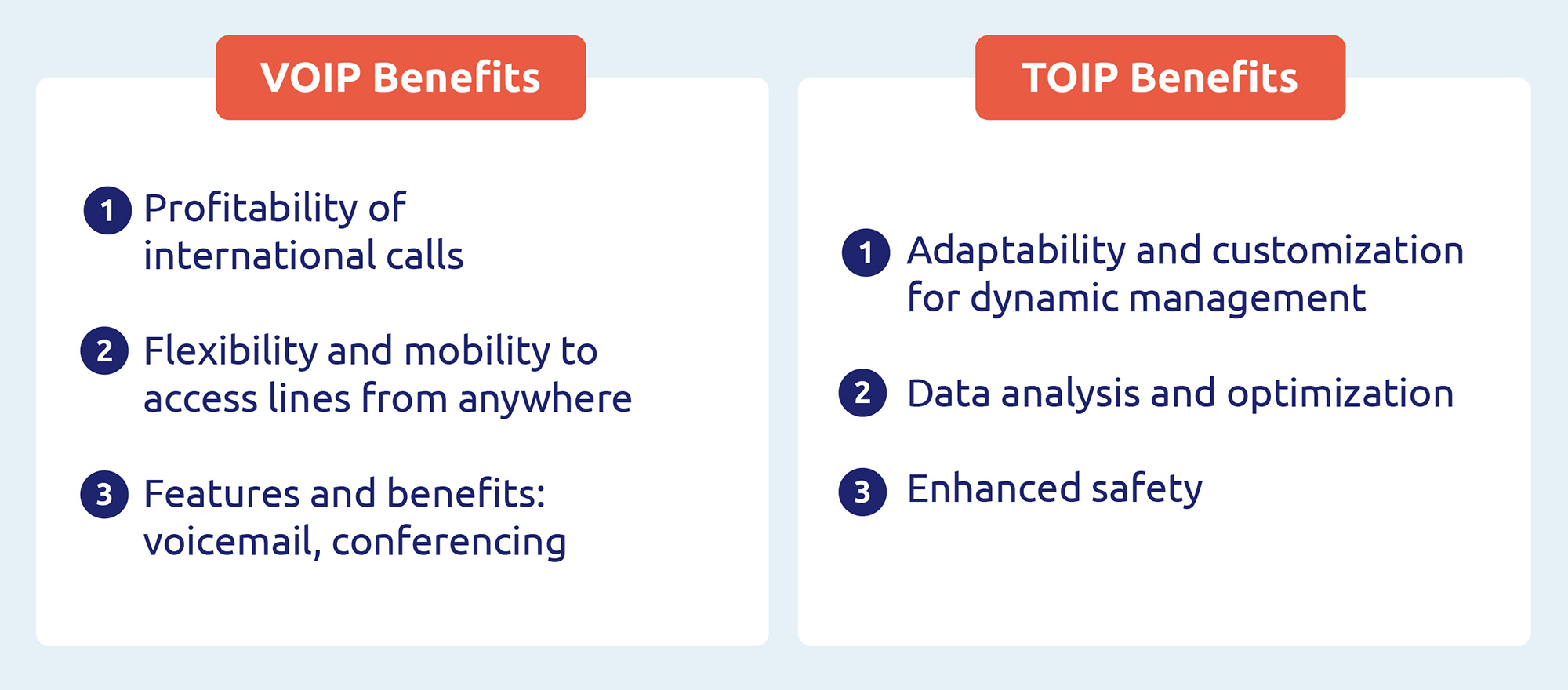
Advantages of VoIP vs. ToIP
When we explore the benefits of Telephony over IP (ToIP) in detail, we discover complementary aspects that reinforce its appeal in the corporate communications landscape.
What are the advantages of ToIP?
ToIP offers greater adaptability to changing business needs, enabling dynamic resource management and real-time evolution of communication capabilities. Its advanced integration with business applications enables advanced personalization of customer interactions, enhancing the overall experience.
A key advantage of ToIP is its ability to provide detailed communications data, offering increased visibility on trends, performance, and bandwidth requirements. This enables companies to make informed decisions to optimize their communications infrastructure and improve quality of service.
What’s more, ToIP enables the implementation of advanced communications security, incorporating robust encryption protocols and protection mechanisms against emerging threats. This enhances the reliability and confidentiality of communications, meeting the growing security requirements of modern businesses.
What are the advantages of VoIP?
One of the main advantages of VoIP is its cost-effectiveness, reducing the cost of international calls and offering more attractive rates for long-distance communications. Moreover, VoIP uses the same network as data, simplifying infrastructure and contributing to operational savings.
Flexibility is another major advantage of VoIP, enabling users to access their business lines anywhere with an Internet connection. This increased mobility encourages remote working and improves employee availability. VoIP also offers advanced features such as conference calling and data transmission during calls, enriching the communication experience.
How ToIP works
Telephony over IP (ToIP) requires specific infrastructure and equipment to ensure efficient, reliable deployment.
Infrastructure and equipment required for ToIP implementation
First and foremost, a robust IP network is essential. It must be able to handle voice traffic with adequate bandwidth to ensure optimum quality of service. ToIP-compatible routers, switches, and firewalls are needed to route traffic securely and efficiently.
A key infrastructure element is the IPBX (Private Branch Exchange over IP), which replaces the PABX. It enables call management, voicemail, and other advanced functions. IP telephones or analog telephone adapters are also required to connect users to the ToIP network.
Audio codecs are another crucial ToIP component, as they enable voice data to be compressed and decompressed. Choosing the correct codec has a direct impact on call audio quality.
Regarding software, ToIP management applications are needed to configure, monitor and administer the system. These applications facilitate extension management, DID (Direct Inward Dialing) assignment, and advanced feature configuration.
ToIP security and reliability
To guarantee secure communications, it is imperative to implement protective measures such as call encryption, robust security protocols, and firewalls specifically designed for ToIP. These devices aim to prevent potential attacks such as call interception or network intrusions, thus ensuring the confidentiality of exchanged voice information.
The reliability of ToIP depends heavily on the stability of the underlying IP network. Sufficient bandwidth, low latency, and efficient traffic management are essential to avoid problems such as outages, call delays, or degraded voice quality. We recommend choosing ISPs offering stable, reliable connectivity to ensure an uninterrupted ToIP experience.
In addition, implementing backup and recovery mechanisms in the event of system failure is crucial to ensure operational continuity. Incident management procedures, including proactive network monitoring and rapid resolution of potential problems, also contribute to ToIP system reliability.
Choosing between VoIP and ToIP
ToIP and VoIP largely depend on a company’s specific needs and strategic objectives.
Criteria for choosing between VoIP and ToIP
A small business or personal user may find VoIP sufficient for simple communications, offering an economical and easy-to-implement solution for voice calls.
On the other hand, for medium-sized to large companies, ToIP offers significant advantages thanks to its deeper integration with IT systems. ToIP excels in complex business environments, offering advanced process automation, personalized customer interactions, and closer team collaboration.
The nature of communications, the size of the business, requirements for advanced functionality, security, and integration with other applications all need to be carefully assessed. It is also essential to consider the company’s future growth and the flexibility required to adapt to technological evolutions.
Overview of future trends in VoIP and ToIP with the emergence of AI
The future of Voice over IP (VoIP) and Telephony over IP (ToIP) is closely linked to the growing emergence of artificial intelligence (AI). Future trends in these technologies promise a deeper convergence with AI, paving the way for more advanced functionalities and enhanced user experiences. Integrating AI into VoIP and ToIP could enable features such as automatic call transcription, voice recognition for more complex commands, and even more intelligent automated response systems.
The personalization of customer interactions will benefit from AI, enabling a finer understanding of individual user needs for more tailored communication experiences. AI-powered anomaly detection systems will also enhance communications security by quickly identifying unusual behavior.
Conclusion: which system to choose between VoIP and ToIP?
In conclusion, VoIP and ToIP are emerging as essential pillars for customer service, offering distinct advantages tailored to the varied needs of businesses. With its simplicity and flexibility, VoIP continues to thrive in more informal contexts, while ToIP is positioning itself as the solution of choice for companies seeking deep integration and advanced process automation.
The growing convergence of these technologies with artificial intelligence promises a future where personalized interactions and more advanced functionalities will play a central role. By navigating between deployment choices, security, and adaptation to future trends, businesses can optimize their communications infrastructure for greater efficiency in a constantly changing environment.
Learn more about the differences between VoIP and ToIP!



